Direct vs. Indirect Hernia: Understanding the Differences
Hernias are a common medical condition that can affect individuals of any age. While the term “hernia” might sound straightforward, there are different types that vary in cause, anatomy, and treatment.
Among the most frequently discussed types are direct and indirect hernias. Though they both occur in the groin region, they differ in several key aspects.
This blog will take you through a comprehensive comparison of direct and indirect hernias, helping you understand the distinctions and how they’re managed.
What is a Hernia?
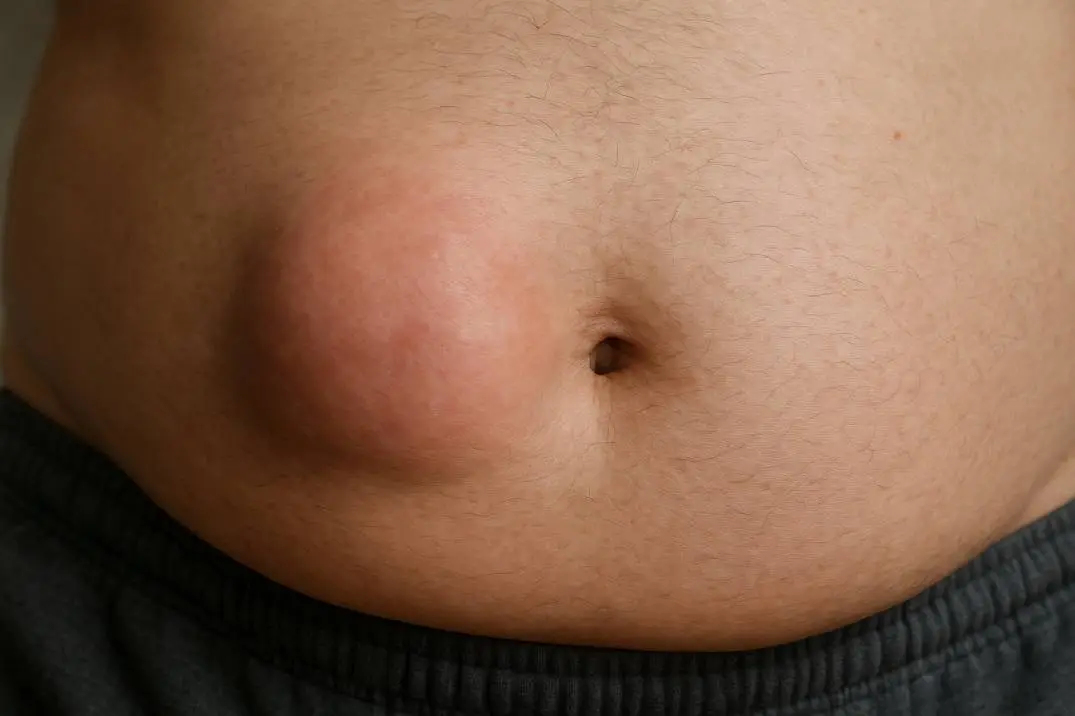
A hernia occurs when an organ or tissue pushes through a weak spot in the muscle or connective tissue that surrounds it.
They are most commonly observed in the abdominal area, where weakened muscles allow parts of intestines or fatty tissue to protrude. Hernias may vary in size and severity and are often noticeable as a bulge under the skin.
While most hernias are not immediately life-threatening, they don’t resolve on their own and usually require medical intervention to prevent complications.
Understanding Direct and Indirect Hernias
Hernias in the groin area fall under a category known as inguinal hernias, and these can be further classified as direct or indirect. The distinction lies in their anatomical location and the path the herniated tissue takes.
Direct Hernia
- Definition: A direct hernia occurs when abdominal contents push through a weakened spot in the abdominal wall, specifically the area of the inguinal canal known as the Hesselbach triangle.
- Anatomy: Found closer to the centre of the groin, direct hernias result from a weakness in the abdominal muscle, leading to a bulge directly through the abdominal wall.
Indirect Hernia
- Definition: An indirect hernia occurs when abdominal contents protrude through the inguinal canal itself and often follow the path that the testicles took during development.
- Anatomy: These hernias originate at the internal inguinal ring, an anatomical opening within the abdominal wall, travelling along the inguinal canal. Indirect hernias can extend into the scrotum in males.
Key Differences Between Direct and Indirect Hernias
Understanding the distinctions between these two types of hernias is critical for proper diagnosis and treatment. Here are the primary differences:
|
Aspect |
Direct Hernia |
Indirect Hernia |
|
Pathway |
Pushes through a weakness in the Hesselbach triangle |
Follows the inguinal canal, through the internal inguinal ring |
|
Congenital vs. Acquired |
Typically acquired due to muscle weakness over time |
Often congenital, linked to incomplete closure of the inguinal canal during development |
|
Risk Groups |
Common in older adults |
Frequently seen in younger individuals, including infants |
|
Gender Prevalence |
More common in males |
Also more frequent in males |
|
Scrotum Impact |
Rarely extends into the scrotum |
May extend into the scrotum, especially in males |
Causes and Risk Factors
Direct Hernias
Direct hernias are often the result of acquired muscle weakness. Common causes include:
- Ageing: The risk increases as muscles naturally weaken over time.
- Strain: Repeated heavy lifting or intense physical activity can compromise abdominal muscles.
- Obesity and chronic coughing can also weaken the abdominal wall.
Indirect Hernias
Indirect hernias are more likely congenital, stemming from a developmental defect where the inguinal canal fails to close properly after birth. Other contributing factors include:
- Gender: Males are more likely to develop indirect hernias due to the descent of testicles during foetal development.
- Family History: A genetic predisposition may play a role.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Common Symptoms
Both direct and indirect hernias can present with similar symptoms, such as:
- A visible bulge in the groin.
- Pain or discomfort, especially when coughing, lifting, or straining.
- A heavy or dragging sensation in the groin.
Indirect hernias, particularly those that extend into the scrotum, may also cause noticeable swelling in this area.
Diagnostic Tools
Doctors use a combination of physical examination and imaging tests like ultrasound or CT scans to confirm the type and severity of hernia. Straining during the examination may help reveal the hernia more clearly.
Treatment Options
The primary treatment for hernias, whether direct or indirect, is surgery.
Surgical Interventions
1.Open Hernia Repair
Surgeons make an incision near the hernia, pushing the protruding tissue back into place and using stitches or mesh to strengthen the muscle wall.
2.Laparoscopic (Keyhole) Surgery
A minimally invasive option involving small incisions through which a camera and surgical tools are inserted. Recovery is often quicker with this method.
Non-Surgical Approaches
Hernias that don’t cause pain or complications may be managed conservatively with lifestyle changes or wearing a supportive truss. However, surgery is eventually recommended to avoid the risk of strangulation, where blood supply to the herniated tissue is cut off.
Prevention Tips
While not all hernias can be prevented, certain steps can reduce your risk:
1.Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess weight puts undue pressure on abdominal muscles.
2.Lift Properly
Always bend at the knees, not the waist, when lifting heavy objects.
3.Strengthen Core Muscles
Exercises that fortify the abdominal wall can reduce vulnerability.
4.Quit Smoking
Chronic coughing from smoking weakens the abdominal wall.
By staying mindful of these precautions, you can help protect your body from developing a hernia.
Final Thoughts
Direct and indirect hernias, though sharing some similarities, differ significantly in their causes, anatomy, and treatment approaches. Recognising these differences is essential for accurate diagnosis and management.
If you notice any symptoms of a hernia, consult a Hernia specialist in pune promptly to determine the best course of action. With timely treatment and preventative measures, you can minimise the risks of complications and regain your quality of life.

Dr. Aditya Kulkarni
MS, DNB, FRCS, MCh (Surgical Gastroenterology & GI Oncology)
Dr. Aditya Kulkarni is a Consultant of Laparoscopic and Robotic Gastrointestinal, Hepato-biliary-pancreatic, and Cancer Surgeon at the Renowned Oasis Surgery Clinic Pune.
