Decoding Symptoms and Treatments of Stage 4 Stomach Cancer
Stage 4 Stomach Cancer: Symptoms, Treatment Options, and Prognosis Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a malignant condition that develops in the lining of the stomach. With varying incidence rates worldwide, stomach cancer remains a significant health concern, particularly in areas with high infection rates of Helicobacter pylori, a bacterium linked to increased risk.
Aside from H Pylori Infection, other risk factors include smoking, a diet high in salt and processed foods, and a family history of stomach cancer.
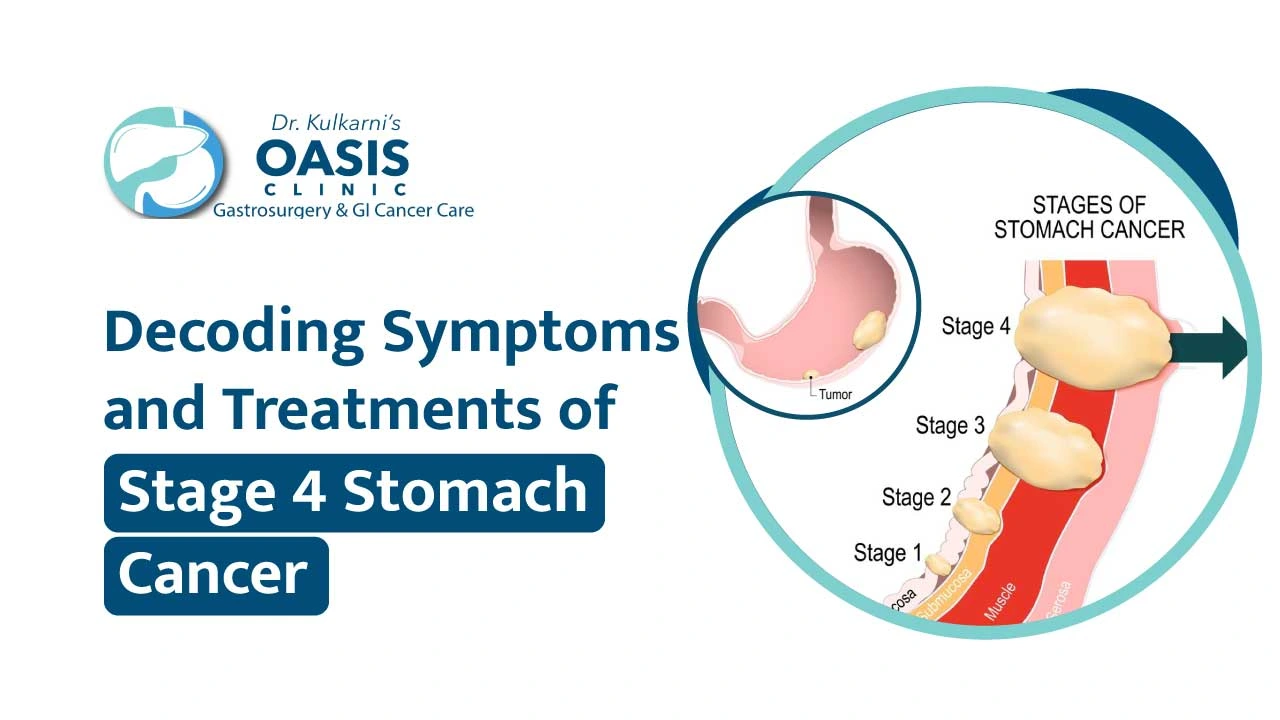
Stage 4 Stomach Cancer represents the most advanced stage of the disease, where the cancer has spread beyond the stomach to distant organs or lymph nodes.Diagnosing stage 4 stomach cancer typically involves imaging studies such as CT scans, endoscopy, and biopsies.
In this Article, we will explore the signs and symptoms of stage 4 stomach cancer, discuss the various treatment options available, and delve into the prognosis for patients facing this challenging diagnosis.
By understanding the complexities of stage 4 stomach cancer, patients can make informed decisions to manage the disease.
Let’s Start Straight Away.
Diagnosing stage 4 stomach cancer
Stage 4 stomach cancer, also known as advanced or metastatic gastric cancer, is the most advanced stage of the disease. At this stage, the cancer has spread beyond the stomach to distant organs such as the liver, lungs, bones, or distant lymph nodes. The cancer may have also invaded nearby structures like the Esophagus, Pancreas, and Colon.
Diagnosing stage 4 stomach cancer involves a combination of physical examination, patient history, and various diagnostic tests. Some of the key diagnostic methods include:
Endoscopy: A flexible tube with a camera (endoscope) is inserted through the mouth and into the stomach, allowing the doctor to visually examine the stomach lining and identify any abnormal growths or lesions. If suspicious areas are found, a biopsy can be performed during the endoscopy to collect tissue samples for further analysis.
Imaging studies: CT scans, MRI, and PET scans are used to visualize the extent of cancer and determine whether it has spread to other organs or lymph nodes. These imaging studies can help in staging cancer and guiding treatment decisions.
Biopsy: A biopsy involves removing a small sample of tissue from the tumour or suspicious area for examination under a microscope. This helps confirm the presence of cancer cells and may provide information on the cancer’s aggressiveness and molecular characteristics, which can influence treatment options.

Blood tests: Blood tests, including complete blood count (CBC) and liver function tests, may be conducted to assess the patient’s overall health and monitor for potential complications related to Stomach Cancer.
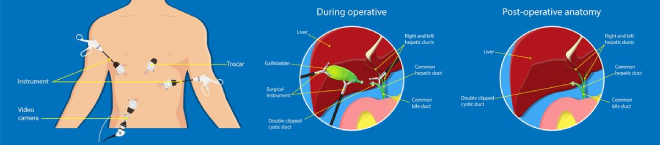
Laparoscopy: In some cases, a Laparoscopy may be performed to further evaluate the extent of cancer spread within the abdominal cavity. A small incision is made in the abdomen, and a Laparoscope (a thin tube with a camera) is inserted to directly examine the organs and tissues.
Once the Diagnosis of Stage 4 Stomach Cancer is Confirmed, the cancer-treating team will work closely with the patient to develop a personalized treatment plan based on the specific circumstances and needs of the individual.
Signs and Symptoms
The most common signs and symptoms of stage 4 stomach cancer may include:
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Persistent indigestion, heartburn, or nausea
- Loss of appetite or feeling full quickly after eating
- Unexplained weight loss
- Vomiting, which may contain blood
- Difficulty swallowing or pain when swallowing
- Fatigue or weakness
- Anemia (low red blood cell count) due to gastrointestinal bleeding
- Swelling in the abdomen, legs, or ankles caused by fluid buildup (ascites or edema)
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes) if the liver is affected
The symptoms of Stage 4 stomach cancer can vary depending on the location of the cancer and how far it has spread. For instance:
- If the cancer has spread to the liver, patients may experience symptoms such as Jaundice, abdominal pain, and swelling due to fluid buildup.
- If the cancer has invaded nearby structures like the esophagus or colon, patients may experience difficulty swallowing, pain when swallowing, or changes in bowel habits.
- If the cancer has metastasized to the lungs, patients might experience shortness of breath, coughing, or chest pain.
- If the cancer has spread to the bones, patients may suffer from bone pain or an increased risk of fractures.
It is important to note that some of these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions. Therefore, if you experience any persistent or concerning symptoms, it is crucial to consult a Robotic GI Surgeon for a proper evaluation and diagnosis.
Treatment Options in stage 4 stomach cancer
Treatment Options for Stage 4 Stomach Cancer are primarily focused on relieving symptoms, prolonging survival, and improving the patient’s quality of life. The choice of treatment depends on the patient’s individual circumstances, such as the extent of cancer spread, overall health, and personal preferences.
Some of the most common treatment options include:
Surgery: While curative surgery is generally not an option for stage 4 stomach cancer, palliative surgery may be performed to alleviate symptoms and improve the patient’s quality of life.
This may include procedures to remove a part of the stomach (partial gastrectomy) or Bypass the Obstructed area (gastrojejunostomy) to help with digestion and food intake.
Take a Moment to Call Someone You Care About
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy drugs work by killing rapidly dividing cancer cells or stopping their growth. In stage 4 stomach cancer, chemotherapy may be used to shrink tumors, slow cancer progression, and relieve symptoms. It can be administered either systemically (through the bloodstream) or regionally (directly into the abdominal cavity).
- Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to target and destroy cancer cells. Although not commonly used as a primary treatment for stage 4 stomach cancer, it may be utilized in combination with chemotherapy (chemoradiation) or as a palliative measure to control symptoms such as pain or bleeding.
- Targeted therapy: Targeted therapies are drugs that specifically target the molecular abnormalities driving cancer growth and spread. For example, trastuzumab (Herceptin) may be used for patients with HER2-positive stomach cancer, while ramucirumab (Cyramza) targets the blood vessels that supply nutrients to the tumor.
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy aims to boost the patient’s immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. Some immunotherapy drugs have shown promise in treating advanced stomach cancer, particularly for patients with specific biomarker profiles.
- The type of treatment chosen for stage 4 stomach cancer will depend on the patient’s individual circumstances, including the extent of the tumour, overall health, and personal preferences.
A multidisciplinary team of cancer experts will work together to develop a personalized treatment plan that balances potential benefits with the side effects and risks associated with each treatment option.
Open communication and shared decision-making between the patient and their cancer team are crucial in navigating the complex landscape of stage 4 stomach cancer treatment.
-
Prognosis in stage 4 stomach cancer
The prognosis for patients with stage 4 stomach cancer is generally less favorable compared to earlier stages of the disease, as the cancer has already spread to distant organs or lymph nodes.
However, it is important to note that the prognosis can vary depending on several factors related to the patient’s individual circumstances. These factors include:- Cancer stage: The extent of cancer spread and involvement of nearby structures or distant organs can significantly impact the prognosis. Patients with limited metastasis may have better outcomes than those with widespread cancer.
- Patient’s age and overall health: Younger patients and those in good general health are often better equipped to tolerate aggressive treatments and may have a more favorable prognosis.
- Type of treatment received: The choice of treatment and the effectiveness of the therapy can influence the patient’s prognosis. Some patients may respond well to specific treatments, such as targeted therapy or immunotherapy, which can lead to improved outcomes.
- Molecular characteristics of the tumor: Certain molecular markers or genetic mutations within the tumor can affect the cancer’s behavior and response to treatment. For example, patients with HER2-positive tumors may benefit from targeted therapy with trastuzumab, potentially improving their prognosis.
- Performance status: A patient’s ability to carry out daily activities and maintain a reasonable quality of life can also impact their prognosis. Patients with a good performance status may be better candidates for aggressive treatments and have a more favorable outlook.
While the Prognosis for Stage 4 Stomach Cancer remains challenging, advancements in treatment options and personalized therapy approaches have led to improved outcomes for some patients.
It is essential for patients to maintain open communication with doctors, discuss realistic expectations, and focus on quality of life throughout the treatment journey.
Support from family, friends, and support groups can also play a crucial role in coping with the emotional and physical challenges associated with Stage 4 stomach cancer.
Wrapping up
Stage 4 Stomach Cancer presents a significant challenge, but understanding its symptoms, treatment options, and prognosis can help patients and their families navigate this difficult journey. The diagnosis involves a combination of physical examination, imaging studies, biopsies, and blood tests to determine the extent of the Cancer’s spread.
Treatment options focus on alleviating symptoms, prolonging survival, and improving quality of life. These options include surgery, chemotherapy, Radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. Prognosis can vary based on factors such as cancer stage, patient’s age and overall health, treatment received, molecular characteristics of the tumor, and performance status.

Dr. Aditya Kulkarni
MS, DNB, FRCS, MCh (Surgical Gastroenterology & GI Oncology)
Dr. Aditya Kulkarni is a Consultant of Laparoscopic and Robotic Gastrointestinal, Hepato-biliary-pancreatic, and Cancer Surgeon at the Renowned Oasis Surgery Clinic Pune.
Book An Appointment


